Introduction
Sea-faring on sea-going vessels is a specialised field requiring professional nautical knowledge and professional qualifications. One can gain extensive practical knowledge and visit different countries to broaden his/her horizons by working on board a sea-going vessel.
Take container vessels as an example. Each container vessel requires approximately 18 to 24 crew members. The Captain is the head of the vessel who takes charge of both the deck and engineering departments.
Prospect
Seafaring career carries a clear progression pathway and good remuneration. Having accumulated sufficient sea-going experience, seafarers may also turn to the shored-based professional maritime services sector, including maritime law and arbitration, ship management, ship finance, marine insurance and shipbroking, for further career development. These sectors have a great demand for talent with sea-going experience.
Major Duties
Captain
- To navigate and steer ship or similar vessel at sea or on inland waterways;
- To monitor the maintenance and repair of ships to ensure compliance with specifications and regulations;
- To perform monitoring roles to ensure safe loading and unloading of cargoes in accordance with safety regulations, harbour rules and customs procedures; and
- To transmit and receive routine and emergency messages with shore stations and other ships
Chief Mate
- To be on duty at the bridge to ensure safe navigation of the vessel;
- To assist the master in handling all administrative work and external affairs; and
- To ensure safe handling of cargoes and maintain cargoes on board in good condition
Second Officer
- To be on duty at the bridge to ensure safe navigation of the vessel;
- To revise the navigational chart and maintain all navigational devices on board the vessel;
- To devise a navigation plan and prepare a chart as appropriate in accordance with the Captain’s instructions, and to draw or rectify the sea route on the chart;
- To calculate the sailing distance and submit the log book to the master daily; and
- To assist the Chief Mate in the safe handling of cargoes and maintaining cargoes on board in good condition
Third Officer
- To be on duty at the bridge to ensure safe navigation of the vessel;
- To maintain all fire-fighting equipment and evacuation facilities; and
- To assist the Chief Mate in the safe handling of cargoes and maintaining cargoes on board in good condition
Cadet
- To study navigational duties under the direction of the Chief Officer;
- To perform maintenance on deck;
- To ensure proper maintenance of appliances, such as recording of expiry dates and defect checking for life saving and firefighting appliances;
- To assist in pilotage operation; and
- To carry out paper work, including filling in relevant forms and documents
Entry Requirement
Deck Officers, Seagoing Vessels
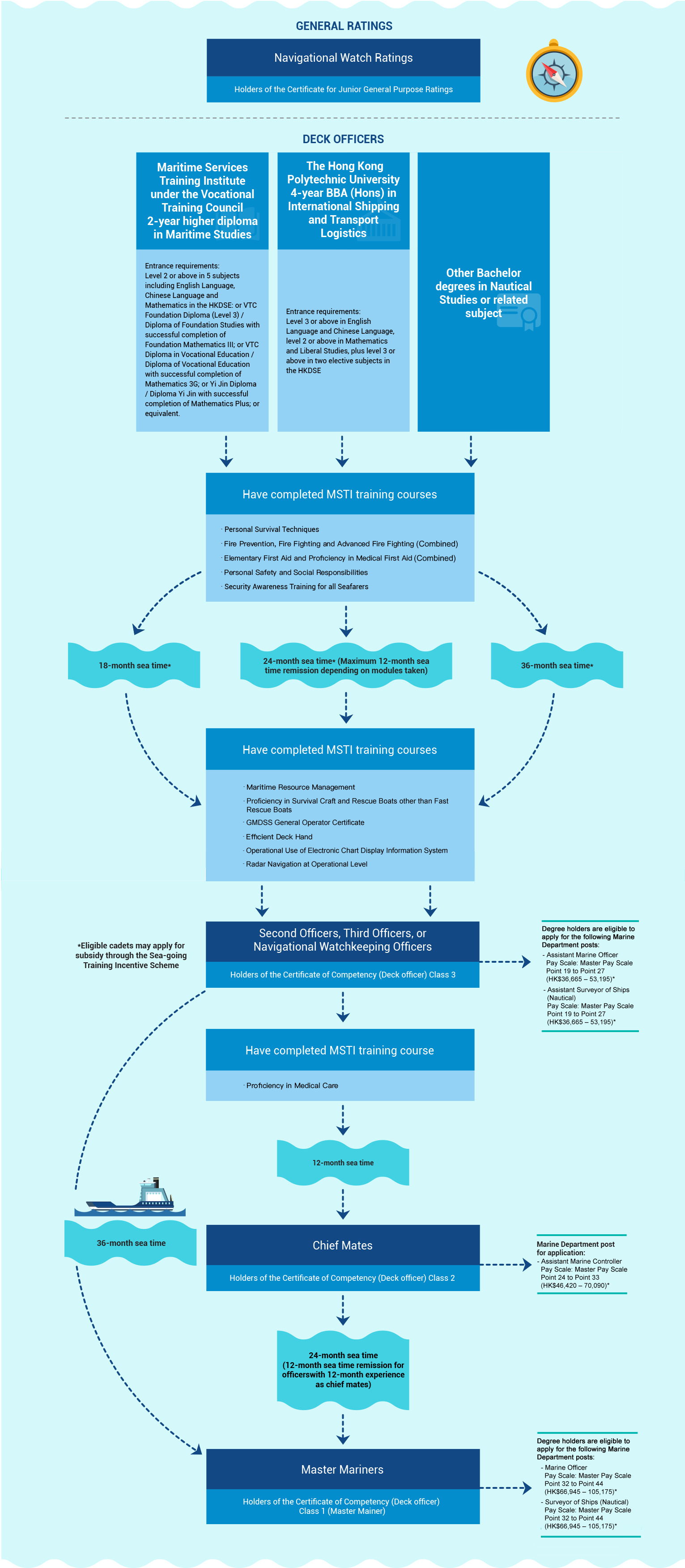
To become a deck officer, one must first complete recognised maritime programmes and the specified pre-sea training, and serve as a cadet in the deck department on board a sea-going vessel to receive in-service training. Having obtained sea-going experience of 18 to 24 months (depending on the maritime course taken), the cadet may apply for the examination for a Certificate of Competency (Deck Officer) (Sea-going) Class 3. Upon passing the examination, the cadet is eligible to serve as a third officer or a second officer. The subsequent examinations for Certificate of Competencies (Deck Officer) Classes 2 and 1 require additional sea-going experience of 1 year and 2 years respectively. After obtaining the Class 1 certificate, the officer is eligible to serve as a Captain.
Career Path- Deck Officers, Seagoing Vessels
Chart
Professional Maritime Qualifications
Commencing 3 September 2018, the following seagoing Certificates of Competency (CoCs) and their Qualification Framework (QF) Level are as follows –
- Certificate of Competency (Deck Officer) Class 1 (Master Mariner) ‐ QF Level 5
- Certificate of Competency (Deck Officer) Class 2 ‐ QF Level 5
- Certificate of Competency (Deck Officer) Class 3 ‐ QF Level 4
Related Courses
Government Subsidy
Qualified sea-going cadets may apply for subsidy under the「Sea-going Training Incentive Scheme」 and receive a monthly incentive award of HK$6,000 during the training period. Moreover, cadets who have successfully passed the Class 3 Deck Officer Examination can apply to the Marine Department for the reimbursement of the first examination fee.
Engineering Crew
Chief Engineer
- To handle all administrative work of the engineering department;
- To repair and maintain all machinery and electrical appliances on board the vessel to ensure their normal operation; and
- To make sure that there is sufficient fuel reserve on board the vessel
Second Engineer
- To assist the Chief Engineer in handling the administrative work of the engineering department;
- To be accountable to the Chief Engineer and repair and maintain all machinery, electrical appliances and engine room facilities on board the vessel; and
- To be on duty at the engine room when necessary so as to ensure the normal operation of all machinery, electrical appliances and facilities
Third Engineer, Fourth Engineer
- To assist the Second Engineer in repairing and maintaining all machinery, electrical appliances and engine room facilities on board the vessel; and
- To be on duty at the engine room when necessary so as to ensure the normal operation of all machinery, electrical appliances and facilities
Cadet
- To study duties related to the operation, maintenance and repair of machinery under the direction of the 2nd Engineer;
- To clean the engine room;
- To perform painting and cleaning jobs; and
- To carry out paper work, including filling in relevant forms and documents
Entry Requirement
Marine Engineer Officers, Seagoing Vessels
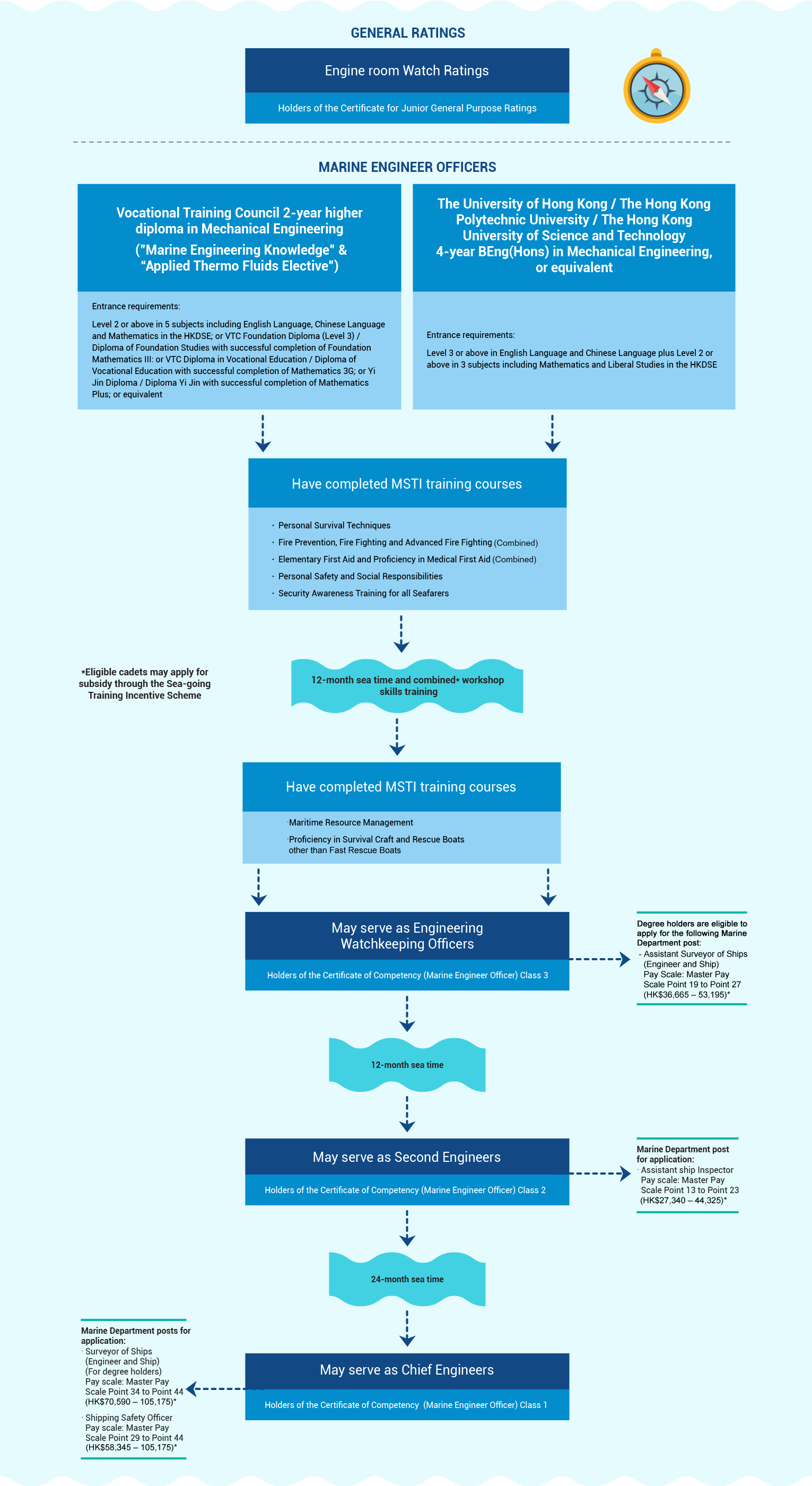
To become a marine engineer officer, one must first complete recognised maritime programmes and the specified pre-sea training, and serve as a cadet in the engineering department to receive training on board a sea-going vessel. Having completed the 1-year integrated workshop skills training and obtained sufficient sea-going experience, the cadet may apply for the examination for a Certificate of Competency (Marine Engineer Officer) (Sea-going) Class 3. Upon passing the examination, the cadet will be eligible to serve as a third engineer or fourth engineer. The subsequent examinations for Certificate of Competencies (Marine Engineer Officer) Classes 2 and 1 require additional sea-going experience of 12 months and 24 months respectively. After obtaining the Class 1 certificate, the officer is eligible to serve as a chief engineer.
Career Path - Marine Engineer Officers, Seagoing Vessels
Chart
Professional Maritime Qualifications
Commencing 3 September 2018, the following seagoing Certificates of Competency (CoCs) and their Qualification Framework (QF) Level are as follows –
- Certificate of Competency (Marine Engineer Officer) Class 1 ‐ QF Level 5
- Certificate of Competency (Marine Engineer Officer) Class 2 ‐ QF Level 5
- Certificate of Competency (Marine Engineer Officer) Class 3 ‐ QF Level 4
Related Courses
- 2-year higher diploma in Mechanical Engineering (Marine Elective), Vocational Training Council
- 4-year BEng(Hons) in Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong/ Hong Kong Polytechnic University / The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Government Funding
Qualified sea-going cadets may apply for subsidy under the Sea-going Training Incentive Scheme and receive a monthly incentive award of HK$6,000 during the training period. Moreover, cadets who have successfully passed the Class 3 Engineer Officer Examination can apply to the Marine Department for the reimbursement of the first examination fee.
Electro-technical Officers
- To assist the Chief Engineer and the Second Engineer in repairing and maintaining all electrical appliances, electronic devices, automated control devices, communication equipment and navigational equipment on board the vessel to ensure their normal operation
- Comparable to a Third Engineer
Entry Requirement - Electro-technical Officers
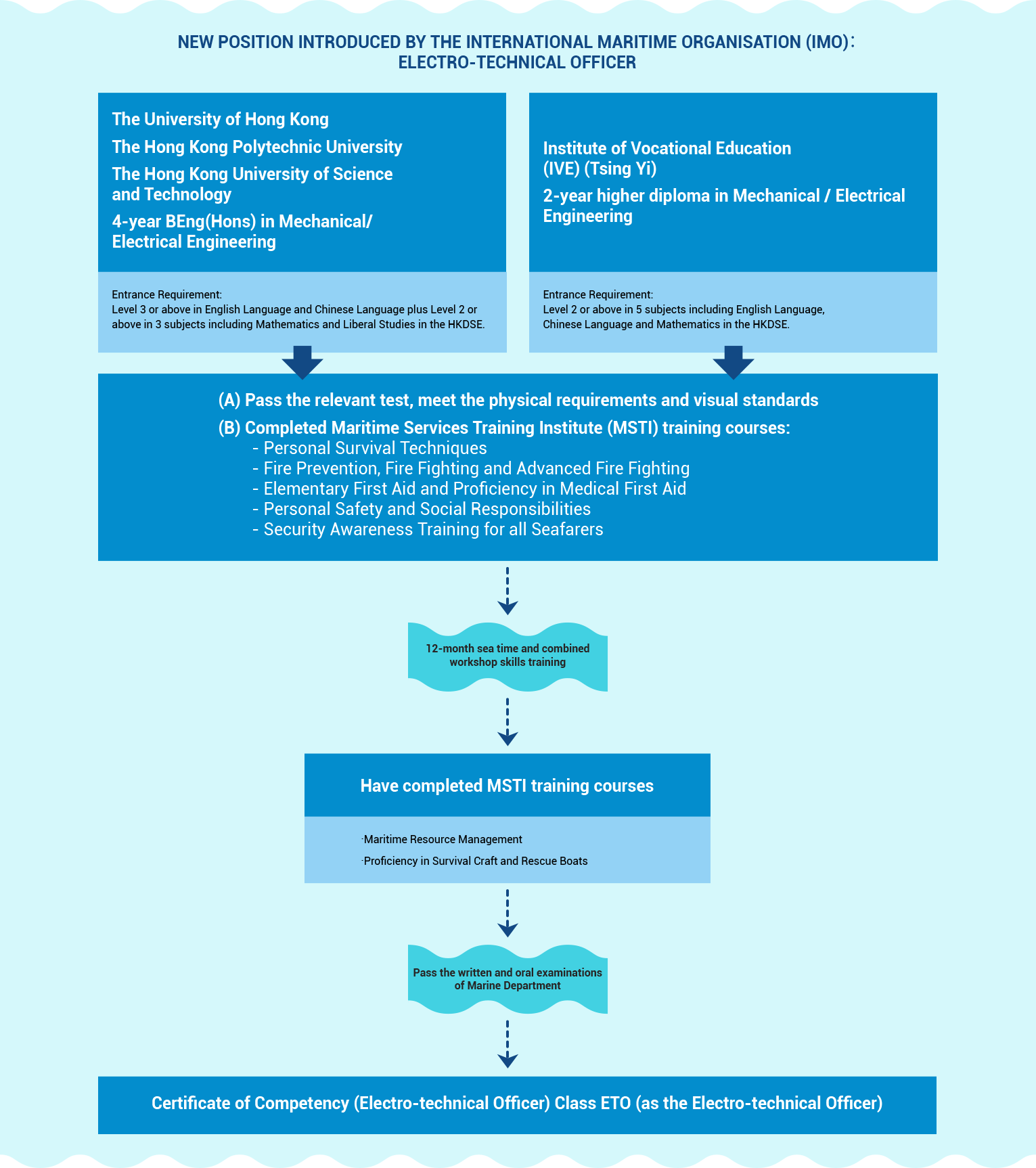
To become an electro-technical officer, one must first complete recognised maritime programmes and the designated pre-sea training, and serve as an electro-technical officer cadet in the engineering department to receive training on board a sea-going vessel. Having completed the 1-year integrated workshop skills training and obtained sufficient sea-going experience, the cadet may apply for the examination for a Certificate of Competency as an electro-technical officer. Upon passing the examination, the cadet will be eligible to serve as an electro-technical officer.
Chart
Professional Maritime Qualifications
Commencing 3 September 2018, the following seagoing Certificate of Competency (CoC) and its Qualification Framework (QF) Level is as follows –
- Certificate of Competency (Electro‐technical Officer) Class ETO ‐ QF Level 4